Environmental chemistry is the research area that monitors emissions of air toxics, clean water supply, global environmental change and waste disposal (including hazardous and radioactive waste management). As aesthetics, economics, recreation, and other elements of better, healthy and safe living become essential issues and have become part of the responsibilities of the modern engineer and scientist, environmental chemistry has risen in importance. In order to minimize and/or eliminate the environmental issues, one has to have great knowledge about chemistry, mechanisms of chemical reactions, flow of energy and materials through the ecosystem and production system. On this occasion, chemistry and materials science have crucial role on decreasing the environmental fates of materials, processes
In Sabancı University, environmental chemistry research is focused mostly on heavy metal removal and membrane technologies.
Research Conducted
Heavy Metal Removal from Polluted Water
In this research area our main purpose is to synthesize, characterize, and investigate the treatment efficiencies of materials in nano size that are cost-effective and environmental friendly and able to remove heavy metals. The following are the studies conducted
- Fast deposition of porous iron oxide on activated carbon by
microwave heating and arsenic (V) removal from water.
Chemical Engineering Journal, 242 : 321-332. ISSN: 1385-8947 - Synthesis and characterization of anatase nano adsorbent and
application in removal of lead, copper and arsenic from water.
Chemical Engineering Journal, 225 : 625-635. ISSN: 1385-8947 - Preparation of graphene oxide/titanium dioxide nanocomposites
adsorption for As (III) ions.
44th World Chemistry Congress, Istanbul, Turkey. - Synthesis and characterization of iron-impregnated pre-oxidized
activated carbon prepared by microwave radiation for As(V)
removal from water.
European Geosciences Union General Assembly 2013, Vienna, Austria - Synthesis of titanium dioxide particles and their application for
simultaneous photocatalytic oxidation of As(III) and sorption of
As(V).
11th National Biorelated Polymer Symposium, 243rd National Spring Meeting of the American Chemical Sociey (ACS), San Diego, USA - Kinetic modeling of arsenic removal from water by ferric ion
loaded red mud.
Seperation Science and Technology, 46 (15): 2380-2390. ISSN: 0149-6395 - Comparative study of arsenic removal efficiency from water
by adsorption and photocatalytic oxidation with titanium
dioxide.
International Conference on Clean Energy (ICCE) 2010, Eastern Mediterranean University, N. Cyprus - Enhanced photocatalytic oxidation of As3+ using titania
nanoparticles for arsenic removal from water.
3rd National Catalysis Congress (NCC), Zonguldak, Turkey - Adsorption mechanism of arsenate on Fe3+ impregnated
activated carbon.
Carbon Materials for Today and Future, Turkish-Japanese Joint Carbon Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey - A parametric evaluation of the removal of As(III) and As(V)
from aqueous water by red mud.
6th Chemical Engineering Conference for collaborative research in Eastern Mediterranean countries: EMCC-6, Belek, Antalya, Turkey
Membrane Technologies
Membrane technologies which are in high favor is being studied. In order to get mechanically and chemically stable, reusable, low energy requiring and cost-effective membranes material development and research plays an crucial role. On that occasion, several studies have been conducted.
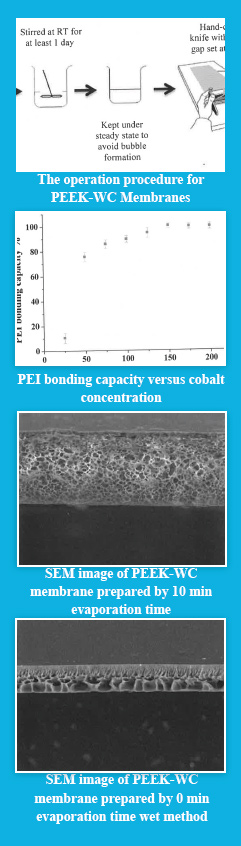
- Modified polyether ether ketone (PEEK-WC) membranes for
ultrafiltration.
Preparation and characterization of modified polyether ether ketone (PEEK-WC) membranes for polymer assisted ultrafiltration of Cu2+ ions from water (2014) - Zeolite membranes for metal ion removal.
Preparation and characterization of modified polyether ether ketone (PEEK-WC) membranes for polymer assisted ultrafiltration of Cu2+ ions from water (2014)
Water Management Studies
It is pretty clear that water severity could not be solved by only developing new technologies to treat the water that has been polluted. It is important to know how much water is used in which process to decrease the water consumption. Accordingly, the following study is conducted.
- Water footprint assessment of Sabanci University.